A Complete Guide to Clinical SAS
This tutorial explains the important topics you need to learn to build a career in clinical SAS.

Clinical SAS is the use of the SAS programming language to manage, analyze and report clinical trial data. SAS is used in the clinical domain for the following tasks:
- Data Management : It can handle large datasets from different sources and formats.
- Statistical Analysis : SAS is used for statistical analyses such as descriptive statistics, regression analysis, survival analysis and analysis of variance (ANOVA) to analyze clinical trial data.
- Safety Reporting : It can generate safety reports and listings to monitor adverse events and safety data during the trial.
- SDTM (Standard Data Tabulation Model) Conversion : It can convert clinical trial data into a format used as a standardized data model for regulatory submission.
- ADaM (Analysis Data Model) Implementation : It can create ADaM datasets which are used for statistical analysis.
- Report Generation : It can prepare clinical trial reports which includes summaries of safety and efficacy (ISS/ISE), clinical study reports (CSRs) and other regulatory documents.
- Automation : SAS macros are created to automate repetitive tasks which leads to improvement in efficiency.
Clinical Trial
A clinical trial is a type of scientific study where researchers test the effectiveness and safety of different medical treatments on volunteers. It can be anything from vaccines, medical devices to screening methods.
Phases of Clinical Trials
Imagine a group of scientists has developed a potential new medicine to treat the flu. They have to follow the following phases of clinic trial to find out if the medicine is safe and effective.
Phase 0 (Microdosing Phase):
- Number of Volunteers : Usually involves 10-15.
- Duration : Typically lasts for a short period, usually a few days to a week.
- Objective : Phase 0 is an exploratory phase that uses subtherapeutic doses of the experimental treatment. The main objective is to obtain early pharmacokinetic (how the body processes the drug) and pharmacodynamic (how the drug affects the body) data. This phase helps researchers understand how the drug behaves in the body and how it's metabolized before moving on to larger Phase 1 trials.
Phase 1 (Human Pharmacology Trials):
- Number of Volunteers : Usually involves a small number of healthy volunteers (20-100).
- Duration : Typically lasts 6 to 12 months.
- Objective :Safety and dosage. The main objective of Phase 1 is to assess the safety of the new treatment or intervention. Researchers want to understand how the treatment is processed by the body (pharmacokinetic), how it behaves at different doses (pharmacodynamic) and whether there are any harmful side effects. Efficacy is not the primary focus of this phase.
- % Continuation : Around 70% of the drugs move to the next phase.
Phase 2 (Therapeutic and Exploratory Trials):
- Number of Volunteers : Enrolls a larger group of patients (100-300).
- Duration : Can last from 6 months to several years.
- Objective :Efficacy and side effects. In Phase 2, the main focus is to evaluate the treatment's effectiveness and further assess its safety. Researchers aim to gather more data on how well the treatment works in treating the target condition or disease and identify the optimal dosage range.
- % Continuation : Around 33% of the drugs move to the next phase.
Phase 3 (Therapeutic Confirmatory Trials):
- Number of Volunteers : Involves an even larger group of patients, often thousands (1000-3000).
- Duration : Can last from one to four years, depending on the complexity of the trial and the number of participants.
- Objective :Efficacy and monitoring of adverse reactions. The main objective of Phase 3 trials are to confirm the effectiveness of treatment in a larger and more diverse (heterogeneous) population. Researchers gather more data on safety and efficacy to establish the treatment's benefits and monitor for any adverse reactions in a larger and more diverse population.
- % Continuation : Around 25-30% of the drugs move to the next phase.
Phase 4 (Post-Marketing Surveillance):
- Number of Volunteers : Larger participants as the treatment is now available to the general public.
- Duration : Several years.
- Objective :Long-term safety and efficacy. The main objective of Phase 4 is to continue monitoring the treatment's safety and efficacy in real-world settings. Researchers collect data on its long-term effects, potential rare side effects and interactions with other medications.
Clinical Trial Study Design
Clinical trial study design is used to find out how the trial will be conducted, what data will be collected and how the results will be analyzed and interpreted. It is to check the safety, efficacy and effectiveness of a medical intervention or treatment. Following are some common types of clinical trial study designs.
- Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT) : Participants are randomly assigned to different groups for comparison of treatment effectiveness.
- Double-Blind Trial : Participants and researchers are unaware of who receives the treatment or control to reduce bias.
- Crossover Trial : Participants receive multiple treatments in randomized order for chronic conditions.
- Parallel Group Trial : Participants are divided into different groups. Each group receives a different treatment throughout the study.
- Non-Randomized Trial : Participants are assigned to treatment groups based on specific criteria when randomization is not possible or ethical.
- Single-Arm Trial : All participants receive the same treatment without a control group. It is used in early-phase safety assessments.
CDISC Standards
CDISC is a worldwide non-profit organization responsible for creating data standards in the pharmaceutical industry. There are three distinct standard data models developed by CDISC specifically for regulatory submissions.
- Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM): Standard structure for clinical trial data sent to regulatory authorities like FDA in data submission package. It is the raw data for regulatory submission.
- Analysis Data Model (ADaM): Uses SDTM domains to develop data sets for summarizing and analyzing clinical data. ADaM data sets support the trial analysis.
- Define-XML: It provides machine-readable version of SDTM and ADaM data set specifications and complex data derivations. It helps FDA work efficiently with data submission.
What is SDTM?
SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model) is a standard for pharmaceutical companies to submit data to FDA (Food and Drug Administration). In other words, it is a widely accepted standard used to structure and present data in a consistent format when submitted to regulatory agencies. It also makes data sharing and comparisons easier. It standardizes variables like demographics, adverse events and medical history.
What is ADaM?
In clinical programming, ADaM stands for Analysis Data Model. It is an industry standard designed to structure data specifically for statistical analysis and reporting purposes.
Difference between STDM and ADaM
- Data: SDTM standardizes variables such as demographics, adverse events and medical history. Whereas ADaM standardizes analysis datasets such as efficacy, safety and trial design.
- Purpose: SDTM is focused on organizing and standardizing data collected during clinical trials for regulatory submissions. Whereas ADaM is designed to structure data specifically for statistical analysis and reporting purposes.
Important Documents for SDTM and ADaM
Below is a list of some important documents required for creating SDTM and ADaM.
- Protocol: This is a detailed summary and guide for the study. It includes information about how the study is designed, when assessments will take place and the methods used for analysis. Before anything else, this Protocol needs to be reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Boards (IRBs), regulatory authorities and the study sites.
- Blank Case Report Form (CRF): The Blank CRF is a form used to collect information from each patient participating in the study. The data manager creates this form and then it's checked by statistical programmers, biostatisticians and other relevant team members to ensure all necessary data for analysis is being captured. Finalizing the CRF can only happen after the Protocol is fully established.
- Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP): The SAP is a plan created by the study's biostatistician. It outlines how the study data will be analyzed and interpreted.
- Table, Figure and Listing templates (TFLs): These templates are designed by the study's biostatistician to provide detailed content for statistical programmers. The programmers will use these templates to create actual tables, figures and listings once the SAP is stable.
- SDTM Annotated Case Report Form (SDTM aCRF): The SDTM aCRF is a version of the Case Report Form that has been annotated by the statistical programmer. It helps the programmer understand and create the structure of SDTM domains.
- SDTM Specifications: These specifications contain details on how to generate the SDTM domains. They cover important information like how to program all the domains, the lengths of variables, labels, formats and instructions on how to create each variable. These specifications are developed by the statistical programmer in conjunction with the SDTM aCRF, as both documents are closely related and depend on each other.
- ADaM Specifications: These specifications provide information about the analysis data sets from SDTM domains, as well as any new variables and derivations needed for the analysis in ADaM data sets. The statistical programmer creates these specifications, but they can only be generated once the SAP and TFL shells are stable.
- Define-XML: This is a machine-readable version of specifications which includes both the SDTM Define-XML document and the ADaM Define-XML document. It provides more detailed information about how the data was created and structured.
Process Workflow
The work process starts with the Case Report Form (CRF) which is used to collect raw data from clinical trials conducted at various sites worldwide.
Once the CRF is ready and data is gathered, the clinical statistical programmer uses this data to create standardized groups of information called Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM) domains. These domains organize the data in a consistent manner.
Later the clinical statistical programmer creates Analysis Data Model (ADaM) data sets from the SDTM domains to support the analysis of the clinical trial data. Then, the clinical statistical programmer generates the Tables, Figures and Listings (TFLs) that need to be included in the clinical study report submitted to regulatory authorities for assessing the safety and efficacy of the study drug.
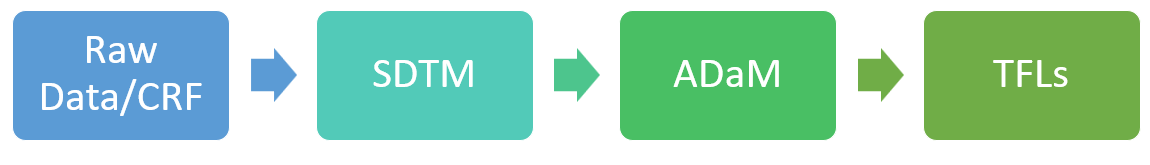
Steps to Generate SDTM Datasets
Following are the steps to generate SDTM datasets from raw data.
- Define Variables and Domains: It's important to review the SDTM documentation to identify the necessary variables and domains based on the data collected during the clinical trial. Common domains typically include Demographics (DM), Adverse Events (AE), Exposure (EX), Disposition (DS).
- Transform Raw Data: It involves tasks such as data cleaning, variable mapping and implementing SDTM-specific rules and formats to convert the raw data into SDTM dataset.
- Apply Guidelines: Make sure to follow the rules set by CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium) for each domain. It includes assigning variables to their datasets and domains following the CDISC standards.
- Perform Validation: It includes comparing the transformed data against SDTM guidelines and running checks to make sure the accuracy of the datasets.
- Generate Define.XML and Documentation: The Define.XML files provide important metadata and detailed descriptions of the SDTM datasets which are needed for regulatory submissions and data interpretation.
Steps to Perform Survival Analysis
Survival analysis is the statistical technique commonly applied in the clinical domain. It analyzes the time it takes for an event of interest to occur such as time to death or time to a specific medical event. Following are the steps involved in performing survival analysis.
- Import Data: Load your data into SAS using PROC IMPORT. The data must include information about the event of interest (start and end time, event status) and any covariates (age, gender, treatment).
- Data Preparation: It includes data cleaning, handling missing values and transforming variables.
- Define the Event: The event could be anything like death, failure, relapse, etc. depending on the context of your study.
- Descriptive Analysis: Generate summary statistics and Kaplan-Meier survival curves to understand the overall survival experience of your sample.
- Survival Model Selection: Choose the appropriate survival model for your analysis. It includes the Kaplan-Meier estimator, Cox proportional hazards model or parametric survival models.
- Model Building: Using SAS procedures like PROC LIFETEST for non-parametric analysis, PROC PHREG for Cox proportional hazards models.
- Interpret the Results: Interpret the output generated by SAS procedure to understand the hazard ratios, survival curves. It is also important to calculate the effects of variables on survival.
- Report and Visualize Results: Present your results in a clear and concise manner that includes tables, graphs etc.
Career in Clinical SAS
There are several job roles within the Clinical SAS domain that includes Clinical SAS Programmer, Clinical Statistical Programmer, Biostatistician and Clinical Data Manager.
Skills for a Clinical SAS Programmer
Below are some of the important skills required for a Clinical SAS Programmer role.
- Educational Qualifications : Bachelor's degree in a relevant field such as Computer Science, Statistics, Life Sciences, Mathematics or a related discipline.
- SAS Programming Skills : Proficiency in SAS programming is the core requirement for this role. It includes knowledge of SAS Base programming and familiarity with SAS Macro language.
- Clinical Research Knowledge : Understanding of clinical research processes which includes clinical trial phases, data collection and regulatory guidelines. Knowledge of CDISC standards such as SDTM and ADaM is a must for this role.
- Statistical Analysis : Knowledge of statistical methodologies used in clinical data analysis and ability to apply appropriate statistical tests and interpret statistical results.
Skills for a Biostatistician
Following is a list of the skills required for a Biostatistician.
- Educational Qualifications: Master's or Ph.D. in Statistics, Life Sciences, Mathematics or a related discipline.
- Statistical Knowledge: A deep understanding of statistical techniques is a must for a BioStatistician's role. It includes proficiency in hypothesis testing, regression analysis, survival analysis, experimental design and multivariate analysis.
- Understanding of Clinical Trials: Knowledge of clinical trial methodologies and regulatory requirements is a must especially for BioStatisticians working in clinical research and drug development.
- Statistical Software: Proficiency in statistical software packages such as SAS, R or Python for performing statistical analysis.
Related Posts : 100+ SAS Tutorials: Step by Step Guide

About Author:
Deepanshu founded ListenData with a simple objective - Make analytics easy to understand and follow. He has over 10 years of experience in data science. During his tenure, he worked with global clients in various domains like Banking, Insurance, Private Equity, Telecom and HR.
While I love having friends who agree, I only learn from those who don't
Let's Get Connected Email LinkedIn




